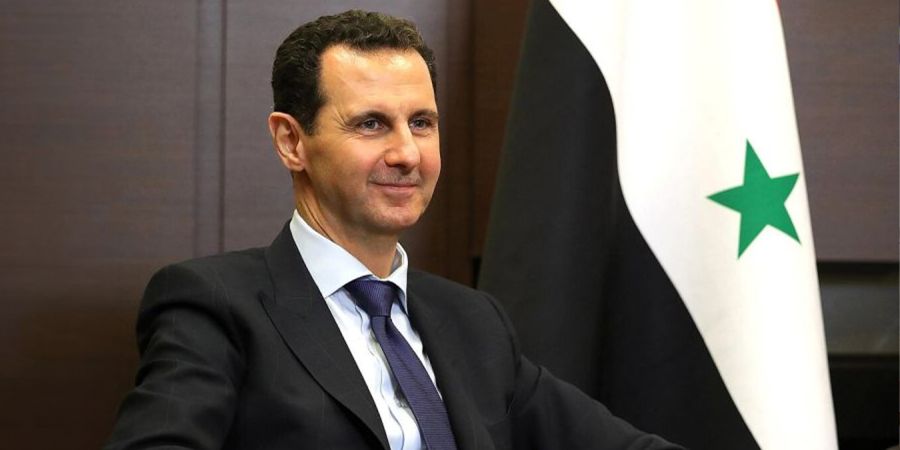
Visit of European Security Official to Damascus
- 13/10/2024
- 5 comments
- 36
- 125


This is Beirut 11:00

This is Beirut 14/01 20:15

This is Beirut 14/01 18:47

This is Beirut 14/01 18:45

This is Beirut 14/01 16:15

This is Beirut 13:12

This is Beirut 12:25

This is Beirut 09:55

This is Beirut 09:40

This is Beirut 09:30
This is Beirut 14/01 18:10
This is Beirut 13/01 21:40
Hala Abdallah 13/01 13:10
Chelsea Al Arif 13/01 12:45

This is Beirut 14/01 18:15

This is Beirut 14/01 15:40

This is Beirut 14/01 15:30

Christiane Tager 11/01 13:00

Christiane Tager 10/01 18:10

This is Beirut 14:00

This is Beirut 10:30

Marie-Christine Tayah 14/01 18:00

This is Beirut 14/01 16:00

Madeleine Cadoux 14/01 14:00

This is Beirut 12:30

This is Beirut 12:24

This is Beirut 09:45

Makram Haddad 14/01 11:00

This is Beirut 14/01 10:10
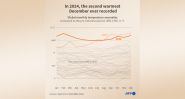
This is Beirut 10/01 11:25

This is Beirut 08/01 10:15

This is Beirut 08/01 09:45

This is Beirut 2024-12-18 19:25

Alain E. Andrea 2024-12-10 19:40

par Ici Beyrouth, 14:00


par Ici Beyrouth, 12:30

par Ici Beyrouth, 12:30

par Ici Beyrouth, 12:25